The book publishing industry has changed significantly over the past twenty years. Technological advancements, changing consumer behavior, and global disruptions from the pandemic and supply chain issues have reshaped how books are produced, consumed, marketed, and sold.
This report outlines the key trends in book sales over the past twenty years and offers insights into how authors and publishers can adapt to current publishing industry trends.
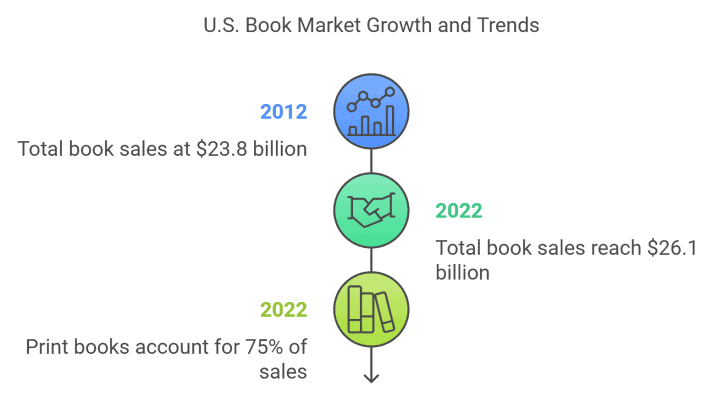
Overall Book Sales Growth
The U.S. book market has experienced modest growth in recent years, particularly following the disruption of the pandemic.
Total book sales in the U.S. reached approximately $26.1 billion in 2022, up from $23.8 billion in 2012¹. This growth reflects a steady recovery and expansion after the initial impact of digital formats and the COVID-19 pandemic.
The overall market growth has been driven by print book sales, which now account for about 75% of total book sales in 2022, compared to 69% in 2012². This resurgence in print book sales indicates a strong consumer preference for physical books, even as digital formats gain traction.
The Resilience of Print Books
While digital formats surged in popularity during the early 2010s, print books have shown remarkable resilience, particularly in adult fiction, children’s books, and genre fiction.
Print book sales in 2022 were 13% higher than pre-pandemic levels (2020), with hardcover books leading the charge³.
The rise of independent bookstores, bolstered by a growing consumer desire for tangible books, has been a significant factor in sustaining print book sales, especially in categories like adult fiction and children’s books⁴. Many independent bookstores have focused efforts on creating community and a place to gather where readers can discover and discuss books in person.
The Growth of Audiobooks
Audiobook sales have been the fastest-growing segment of the book market in the last decade, with a 25% increase in 2022 alone⁵.
The global audiobook market was valued at $6.4 billion in 2022, with projections suggesting a 24% annual growth rate from 2023 to 2030⁶.
Audiobooks are increasingly popular due to the proliferation of smartphones, platforms like Audible, and a consumer desire for more flexible, multitasking-friendly media.
Audiobooks can now be mass-produced using AI at little to no cost for authors and publishers.

E-book Sales Stabilization
After reaching a peak in the mid-2010s, e-book sales have plateaued. As of 2022, e-books accounted for approximately 18% of total book sales in the U.S.⁷.
The market for e-books is now dominated by bestsellers and certain genres, particularly romance, mystery, and science fiction.
Below are examples of bestsellers in these categories that have seen extreme growth in e-book sales:
“It Ends with Us” by Colleen Hoover
Hoover’s romance novel, originally published in 2016, saw a surge in sales in 2021 and 2022, driven by viral trends on platforms like TikTok.
“It Ends with Us“ sold over 3.4 million copies in 2022 alone, with the majority of those sales coming from e-book and audiobook formats⁸. Hoover’s works frequently dominate digital ebook platforms like Kindle Unlimited.
“The Silent Patient” by Alex Michaelides
This psychological thriller, published in 2019, became a bestseller due to its gripping story and strong performance in digital formats.
“The Silent Patient“ sold over 1 million copies in its first year of publication, with a substantial share of these sales attributed to e-books⁹. It consistently ranked among the top-selling e-books on platforms like Amazon Kindle.
“Project Hail Mary” by Andy Weir
Weir’s 2021 science fiction novel continued his success from “The Martian“, becoming a top e-book seller across multiple digital platforms.
“Project Hail Mary“ sold over 1.5 million copies globally in its first six months, with e-book sales comprising a significant portion of this figure¹⁰. The novel’s success demonstrates the ongoing appeal of science fiction in the digital space.
Shifting Consumer Preferences
The rise of direct-to-consumer models, such as subscription services like Kindle Unlimited, BookBub and BookBub Ads, Scribd, Spotify audiobooks, and more has significantly altered book buying habits.
Many readers now prefer the convenience of digital ebooks and audiobooks, prioritizing personalized recommendations from platforms like Amazon and independent digital book retailers. This is especially true as platforms that used to be extremely popular book discovery engines like Goodreads have been outcompeted by other forms of social media and retailers’ book suggestions.
Genre fiction—particularly romance, thriller, and fantasy—continues to be a dominant category, with niche-driven consumer tastes influencing what books are purchased and consumed.
Implications for Authors and Publishers
All these changes have created many opportunities for authors and publishers.
Self-Publishing
The growth of e-books and audiobooks has created new opportunities for self-published authors. Platforms like Amazon’s Kindle Direct Publishing (KDP) and Audible’s ACX allow authors to reach a global audience with minimal upfront costs.
As of 2023, self-published e-books accounted for 35% of all e-book sales on Amazon¹¹ which means self-published e-book sales are now a huge share of the market.
Early Growth of Self-Publishing (2000s – Early 2010s)
The launch of Amazon’s Kindle Direct Publishing (KDP) in 2007 marked a transformative period, allowing authors without traditional book deals to publish directly to a massive audience. This led to a significant rise in the number of self-published books.
Bowker reported a jump from about 150,000 self-published titles in 2010 to over 391,000 by 2012, largely due to the success of e-books and self-publishing’s new accessibility for authors¹².
Expansion and Market Share Increase (2015 – 2020)
By 2015, self-publishing had established itself as a sizable market segment. Nielsen BookScan estimated that self-published titles accounted for 17% of e-book sales by 2016¹³.
Additionally, self-published print books saw an uptick as authors used print-on-demand services through platforms like IngramSpark and CreateSpace (which is now KDP Print). Bowker data showed a near-doubling in self-published print titles from 2015 to 2018, reaching over 1.68 million in 2018¹⁴.
Pandemic Surge (2020 – 2022)
During COVID-19, self-publishing surged as more people turned to reading and writing. In 2021, data from WordsRated and KDP indicated a 25% increase in self-published e-book sales, a shift driven by higher digital consumption during lockdowns¹⁵.
Audiobooks and new distribution channels also expanded self-published sales across formats and regions.
Stabilization and Maturity (2023 – Present)
Self-publishing is now a mature segment with a strong share of digital sales.
Platforms like KDP, Ingramspark, BookBaby, and Smashwords have introduced distribution tools, enabling authors to access even broader markets
Hybrid Authors
Authors who successfully navigate both traditional publishing and self-publishing are benefiting from the best of both worlds: the reach and support of traditional publishers combined with the higher profit margins of self-publishing.
Many authors who have previously been traditionally published are beginning to experiment with self-publishing and reaping the rewards. And there are also many authors who have decided to start with self-publishing unless or until they get a traditional book deal.
Diversity and Inclusivity
There has been a large rise in interest in diversity and inclusivity in the industry among a very vocal portion of consumers. Publishers and authors that create more diverse and inclusive content can tap into underserved markets, especially in the young adult (YA) and LGBTQ+ genres.
Challenges for Traditional Publishers
There are now significant new challenges for traditional publishers because of the growth of self-publishing and other industry changes.
Pricing Pressures
The rise of e-books and audiobooks, coupled with subscription services, has placed considerable pressure on traditional book pricing structures. Many publishers struggle to maintain profit margins, especially as mass-market print editions face competition from cheaper e-books and digital subscription models.
Consolidation and Competition
The increasing dominance of major retailers, particularly Amazon, has led to consolidation in the publishing industry. Smaller, independent publishers face mounting competition as large platforms become primary distributors of both print and digital books.
Impact of Subscription and Streaming Services
Subscription and streaming services are poised to eat away at market share of traditional book retailers.
Growth of Subscription Models
Subscription models like Kindle Unlimited, Audible, and the recently launched Book of the Month have dramatically changed consumer expectations for book access. Authors in these programs see increased discoverability, but the financial model can often be less lucrative than traditional sales.
Piracy and Loss of Control
Digital piracy remains a challenge for both authors and publishers. With increasing digital book consumption, unauthorized sharing and piracy are becoming widespread. Authors and publishers must adapt by implementing DRM (Digital Rights Management) systems and exploring new revenue models as well as using AI and software to monitor and manage piracy.
Emerging Trends
There are two major trends that will continue to impact the industry:
Artificial Intelligence in Publishing
AI tools are beginning to influence multiple areas in the book industry, including book marketing, content discovery, and even content creation. AI tools have already transformed how audiobooks are produced and will continue to evolve at a breathtaking pace as the AI increases its usefulness and as publishers learn how to take advantage of these tools to reduce costs and increase production and marketing output.
The potential use-cases for AI are nearly unlimited and although there has been backlash audiobook narrators and others impacted by AI, the potential to increase profits and productivity will not be ignored by the industry.
AI-driven recommendation engines and personalized reading apps are reshaping how readers discover new books and this will require publishers and authors to adapt their marketing strategies.
Sustainability in Publishing
The environmental impact of paper production is prompting many publishers to explore more sustainable practices. There is growing interest in eco-friendly production methods and materials, particularly in print books.
Conclusion
The book publishing industry has undergone profound transformations over the last decade, driven by the rise of digital formats, changing consumer preferences, and AI.
While print books have made a strong recovery, e-books and audiobooks continue to thrive, particularly in popular genres like romance, mystery, and science fiction.
Authors now have more opportunities than ever to reach global audiences through both traditional publishing and self-publishing. However, these opportunities come with new challenges, such as pricing pressures, piracy, and competition from large platforms like Amazon.
For publishers, the key to success lies in adapting to a rapidly evolving market by experimenting with new ideas and technology, diversifying revenue streams, and using data to better understand consumer behavior.
Footnotes
- Association of American Publishers (AAP), “2023 Annual Report,” AAP.org, 2023
- Association of American Publishers (AAP), “2012 Book Sales Report,” AAP.org, 2012
- NPD BookScan, “2022 Print Sales Recovery,” NPD.com, 2022
- The Bookseller, “Indie Bookstore Growth,” TheBookseller.com, 2023
- Statista, “Audiobook Market Trends,” Statista.com, 2023
- Grand View Research, “Global Audiobook Market,” GrandViewResearch.com, 2023
- Association of American Publishers (AAP), “2022 E-book Sales Report,” AAP.org, 2022
- NPD BookScan, “Best-Selling Books of 2022,” NPD.com, 2022
- Michaelides, Alex, The Silent Patient, Celadon Books, 2019
- Weir, Andy, Project Hail Mary, Ballantine Books, 2021
- BookStat, “Self-Publishing Market,” BookStat.com, 2023
- Bowker, “Self-Published Titles in 2012,” Bowker.com, 2013
- Nielsen BookScan, “Self-Publishing Market Share,” Nielsen.com, 2016
- Publishers Weekly “Self-Publishing Is Thriving, According to Bowker Report” Publishersweekly.com, 2023
- Words Rated “Self-published Books & Authors Sales Statistics” Wordsrated.com, 2023
Tom Corson-Knowles is the founder of TCK Publishing, and the bestselling author of 27 books including Secrets of the Six-Figure author. He is also the host of the Publishing Profits Podcast show where we interview successful authors and publishing industry experts to share their tips for creating a successful writing career.
